- 重定向類型
- 在 .htaccess 中設置重寫規則:使用案例
- 為 cPanel 帳戶中的所有網站啟用 HTTPS 重定向
- 為特定網站禁用重寫規則的應用
- 將單個網站從 http:// 重定向到 https:// 或 https://www
- 強制使用 'https://example.com' 或 'https://www.example.com'
- 強制使用 'http://' 或 'http://www.'
- 重定向到/從子域
- 將 http:// 重定向為 https:// 或 https://www,使用 CloudFlare 彈性 SSL 模式
- 為特定子文件夾啟用 HTTPS
- 強制特定頁面的 HTTPS
- 不論位置設置對特定文件名的重定向
- 部分重定向到 https://
- 如何在重寫規則中指定重定向狀態碼
一旦 SSL 證書安裝完畢,並且網站可以通過 https:// 正確訪問,您可能希望默認情況下使其可以通過 https:// 訪問。換句話說,當用戶在瀏覽器中輸入 domain.com 時,應重定向到 https://domain.com 以安全訪問網站。
在本文中,我們將介紹一些基本的 HTTPS 重定向類型,並展示如何使用 .htaccess 在 Cpanel 中強制 HTTPS。
如果您轉到 cPanel >> '文件管理器',可以找到該文件。然後,找到您的網站的文檔根目錄。對於主要的 cPanel 網域,該文件夾通常是 'public_html'。如果網站是附加域,您可以在 '附加域' 部分查找其文檔根目錄。
當您找到該文件夾時,.htaccess 文件 可能已經存在。要確認,請點擊右上角的 '設置',並勾選 '顯示隱藏文件(點文件)'。
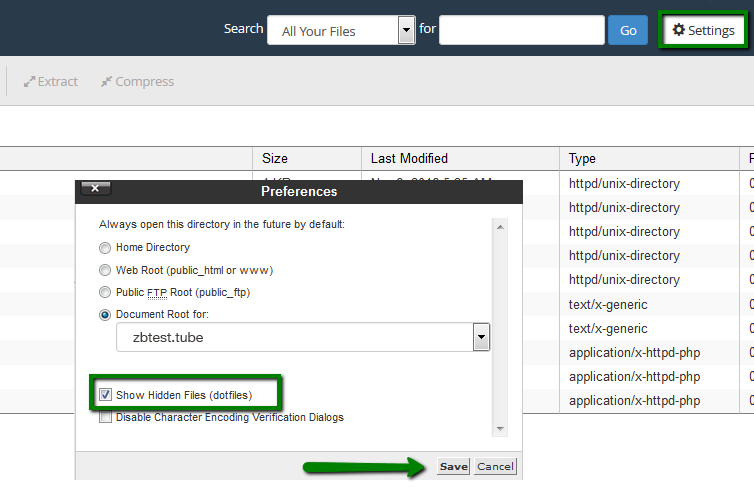
如果該文件未出現,可以通過點擊 '+文件' 來創建它。請確保將文件命名為 '.htaccess',以點開頭。
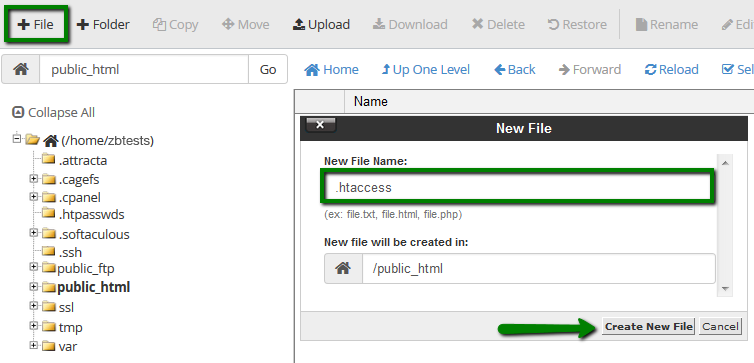
要打開該文件,右鍵單擊它,然後點擊 '編輯'。在彈出的窗口中,點擊 '編輯'。
重定向類型
在設置重寫規則時,了解有永久重定向類型和臨時重定向類型是有用的。每種類型的處理方式在搜索引擎和網頁瀏覽器上各不相同,並且具有自己的狀態碼,可以在重寫規則中明確指定:
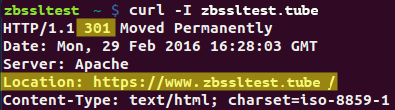
- 狀態碼 301 '永久移動'(永久重定向)意味著所請求的資源永久移動到新位置,因此搜索引擎不應考慮之前位置的引用,並索引新位置。反之,網頁瀏覽器將在緩存中存儲新 URL,因此優先於初始 URL。
- 狀態碼 302 '臨時移動'(臨時重定向)意味著該重定向在有限的時間內設置。在這種情況下,搜索引擎應將兩個位置視為相同,因此初始位置仍然有效。相應地,瀏覽器不會緩存新 URL,並且每次請求初始 URL 時都會執行重定向。
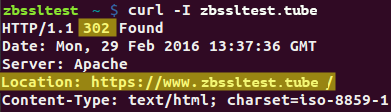
注意:長期啟用 302 重定向可能會顯著降低網站在搜索結果中的排名。在 HTTP-HTTPS 重定向的情況下,所有網站請求均在 http://domain.com 和 https://domain.com 之間分割,因為兩者都被搜索引擎分別編入索引。因此,在大多數情況下,301 狀態碼更適合用於 HTTP-HTTPS 重定向。
我們將在下一部分詳細說明需要指定狀態碼的位置。
在 .htaccess 中設置重寫規則:使用案例
注意:下面指定的指令使用自己的語法。改變任何符號或字符可能導致重寫規則無法正常工作或失敗。為了保持清晰,我們已經用紅色突出顯示了可以修改的部分(主要是應該放置特定域名的地方)。
讓我們概述一下從 HTTP 到 HTTPS 的重定向最常見的配置方式。
為 cPanel 的所有網站啟用 HTTPS 重定向
注意:如果您的 .htaccess 中已經有一些代碼,請將這一部分添加到相似前綴的規則上方。
要為 cPanel 帳戶內的所有網站重定向,可以向 cPanel 的主目錄中的 .htaccess 文件添加以下任一代碼塊('/home/cpanelusername/'):
a)
RewriteEngine On
RewriteCond %{HTTPS} !=on
RewriteRule ^/?(.*) https://%{SERVER_NAME}/$1 [R,L]
這個代碼塊啟用重寫功能,驗證初始請求是否已經是 https://,然後重寫整個請求 URL,將 http:// 替換為 https://(例如,http://domain.com/subfolder/index.php 將被替換為 https://domain.com/subfolder/index.php)。
b)
RewriteEngine On
RewriteCond %{HTTPS} off
RewriteRule (.*) https://%{HTTP_HOST}%{REQUEST_URI} [R,L]
這個代碼塊的工作原理與上面的代碼塊相同,只是使用了不同的語法。您可以使用上述任何一個重寫規則來為 cPanel 帳戶內的所有網站進行重定向。
為特定網站禁用重寫規則的應用
如果您需要為 cPanel 帳戶中的所有網站設置重定向,但不包括 example.com,則可以將下面的代碼塊添加到主目錄的 .htaccess 中:
RewriteEngine On
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^(www.)?example.com|^(www.)?example2.com
RewriteRule .* - [L]
RewriteCond %{HTTPS} !=on
RewriteRule ^/?(.*) https://%{SERVER_NAME}/$1 [R,L]
代碼塊中的第一個條件將請求的 URL 與包含的域名(不應重定向的)進行匹配,如果匹配則停止重寫。您可以在條件指令中使用 '|' 符號分隔域名,或指定多個條件指令(請參見下面的示例)。
a) 用 '|' 分隔域名
RewriteEngine On
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^(www.)?example.com|^(www.)?example2.com
RewriteRule .* - [L]
RewriteCond %{HTTPS} !=on
RewriteRule ^/?(.*) https://%{SERVER_NAME}/$1 [R,L]
b) 指定多個條件
RewriteEngine On
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^(www.)?example.com$ [OR]
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^(www.)?example2.com$
RewriteRule .* - [L]
RewriteCond %{HTTPS} !=on
RewriteRule ^/?(.*) https://%{SERVER_NAME}/$1 [R,L]
.htaccess 重定向將 HTTP 重定向到 HTTPS 或 https://www 的單個網站
a) 將所有 http:// 請求重定向到相同頁面,但使用 https://
RewriteEngine On
RewriteBase /
RewriteCond %{HTTPS} !=on
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^example.com$ [OR]
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^www.example.com$
RewriteRule .* https://example.com%{REQUEST_URI} [R=301,L]
b) 將所有 http:// 請求重定向到相同頁面,但使用 https://www。
RewriteEngine On
RewriteBase /
RewriteCond %{HTTPS} !=on
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^example.com$ [OR]
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^www.example.com$
RewriteRule .* https://www.example.com%{REQUEST_URI} [R=301,L]
.htaccess 強制使用 'https://' 或 'https://www'
a) 將所有 http:// 和 https:// 請求重定向到相同頁面,但使用 https://example.com(同時將 https://www.example.com 重定向到 https://example.com)
RewriteEngine On
RewriteBase /
RewriteCond %{HTTPS} !=on
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^example.com$ [OR]
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^www.example.com$
RewriteRule .* https://example.com%{REQUEST_URI} [R=301,L]
RewriteCond %{HTTPS} =on
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^www.example.com$
RewriteRule .* https://example.com%{REQUEST_URI} [R=301,L]
b) 將所有 http:// 和 https:// 請求重定向到相同頁面,但使用 https://www(同時將 https://example.com 重定向到 https://www.example.com)
RewriteEngine On
RewriteBase /
RewriteCond %{HTTPS} !=on
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^example.com$ [OR]
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^www.example.com$
RewriteRule .* https://www.example.com%{REQUEST_URI} [R=301,L]
RewriteCond %{HTTPS} =on
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^example.com$
RewriteRule .* https://www.example.com%{REQUEST_URI} [R=301,L]
.htaccess 強制使用 'https://' 或 'https://www'
a) 將所有 http:// 和 https:// 請求重定向到相同頁面,但使用 https://example.com(同時將 https://www.example.com 重定向到 https://example.com)
RewriteEngine On
RewriteBase /
RewriteCond %{HTTPS} !=on
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^example.com$ [OR]
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^www.example.com$
RewriteRule .* https://example.com%{REQUEST_URI} [R=301,L]
RewriteCond %{HTTPS} =on
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^www.example.com$
RewriteRule .* https://example.com%{REQUEST_URI} [R=301,L]
b) 將所有 http:// 和 https:// 請求重定向到相同頁面,但使用 https://www(同時將 https://example.com 重定向到 https://www.example.com)
RewriteEngine On
RewriteBase /
RewriteCond %{HTTPS} !=on
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^example.com$ [OR]
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^www.example.com$
RewriteRule .* https://www.example.com%{REQUEST_URI} [R=301,L]
RewriteCond %{HTTPS} =on
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^example.com$
RewriteRule .* https://www.example.com%{REQUEST_URI} [R=301,L]
.htaccess 強制使用 'http://' 或 'http://www.'
a) 將所有網站訪問者重定向到相同頁面,但使用強制 http:// + 將 http://www.example.com 重定向到 http://example.com
RewriteEngine On
RewriteBase /
RewriteCond %{HTTPS} =on
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^example.com$ [OR]
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^www.com$
RewriteRule .* http://example.com%{REQUEST_URI} [R=301,L]
RewriteCond %{HTTPS} !=on
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^www.example.com$
RewriteRule .* http://example.com%{REQUEST_URI} [R=301,L]
b) 將所有網站訪問者重定向到相同頁面,但使用強制 http://www + 將 http://example.com 重定向到 http://www.example.com
RewriteEngine On
RewriteBase /
RewriteCond %{HTTPS} =on
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^example.com$ [OR]
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^www.example.com$
RewriteRule .* http://example.com%{REQUEST_URI} [R=301,L]
RewriteCond %{HTTPS} !=on
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^example.com$
RewriteRule .* http://www.example.com%{REQUEST_URI} [R=301,L]
重定向到/從子域
a) 從 example.com 或 www.example.com(包括 http:// 和 https://)重定向到特定子域
RewriteEngine On
RewriteBase /
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^example.com$ [OR]
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^www.example.com$
RewriteRule .* https://subdomain.example.com%{REQUEST_URI} [R=301,L]
b) 從子域(包括 http:// 和 https://)重定向到 https://www.example.com
RewriteEngine On
RewriteBase /
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^subdomain.example.com$
RewriteRule .* https://www.example.com%{REQUEST_URI} [R=301,L]
將 http:// 重定向到 https:// 或 https://www 並使用 CloudFlare 彈性 SSL 模式
a) 基本的 http:// 到 https:// 重定向,但此代碼塊應與 CloudFlare 彈性 SSL 模式一起使用
RewriteEngine On
RewriteBase /
RewriteCond %{HTTPS} !=on
RewriteCond %{HTTP:X-Forwarded-Proto} !https
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^example.com$ [OR]
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^www.example.com$
RewriteRule .* https://example.com%{REQUEST_URI} [R=301,L]
b) 相同的規則,但重定向到 https://www
RewriteEngine On
RewriteBase /
RewriteCond %{HTTPS} !=on
RewriteCond %{HTTP:X-Forwarded-Proto} !https
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^example.com$ [OR]
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^www.example.com$
RewriteRule .* https://www.example.com%{REQUEST_URI} [R=301,L]
為特定子文件夾啟用 HTTPS
有時您可能需要重定向網站中的特定子文件夾,而將其餘部分保持不變。要這樣做,請將以下代碼塊插入到 .htaccess 中:
RewriteEngine On
RewriteCond %{HTTPS} !=on
RewriteRule ^/?subfolder/(.*) https://%www.example.com/subfolder/$1 [R,L]
此規則僅當初始請求中提到指定的子文件夾時才會生效。
.htaccess 強制特定頁面的 HTTPS
重定向特定頁面的重寫規則與前面的類似:
RewriteEngine On
RewriteCond %{HTTPS} !=on
RewriteRule ^example.html$ https://www.example.com/example.html [R,L]
僅請求的頁面會被重定向;其他網站內容將不受影響。
如果需要重定向的頁面位於特定子文件夾中,則 RewriteRule 行應修改如下:
RewriteRule ^test/example.html$ https://www.example.com/test/example.html [R,L]
(在上面的示例中,'test' 是相關的子文件夾)
為特定文件名設置重定向,不論位置
如果您有多個具有相同名稱的頁面,位於不同子文件夾中(下面使用的例子是 'index.html'),您可以為所有頁面啟用 HTTPS 重定向。可通過應用如下規則來達成:
RewriteEngine On
RewriteCond %{HTTPS} !=on
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} index.html
RewriteRule (.*) https://%{HTTP_HOST}%{REQUEST_URI} [R,L]
僅與 {REQUEST_FILENAME} 參數值匹配的文件名頁面將被重定向到 HTTPS。
部分重定向到 https://
a) 將所有網站重定向到 https://,但排除一個頁面(example.com/some_http_page.html)
RewriteEngine On
RewriteBase /
RewriteCond %{HTTPS} !=on
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^example.com$
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_URI} !^/some_http_page.html$
RewriteRule .* https://example.com%{REQUEST_URI} [R=301,L]
b) 僅將一個頁面 example.com/some_https_page.html 重定向到 https://
RewriteEngine On
RewriteBase /
RewriteCond %{HTTPS} !=on
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^example.com$
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_URI} ^/some_https_page.html$
RewriteRule .* https://example.com%{REQUEST_URI} [R=301,L]
如何在重寫規則中指定重定向狀態碼
每條重寫規則都以所謂的「重寫標誌」(在方括號中指定,例如 [R,L])結尾。這些標誌幫助控制正確執行的重寫過程。要設置具有 301 狀態碼(永久)的重定向,您需要通過在方括號中添加 '=301' 將此碼分配給 R-標誌。

注意: 如果沒有為 R-標誌指定值,則默認會執行帶有 302 狀態碼的重定向。
完成後,可以利用 此工具 檢查重定向功能及其狀態碼。
